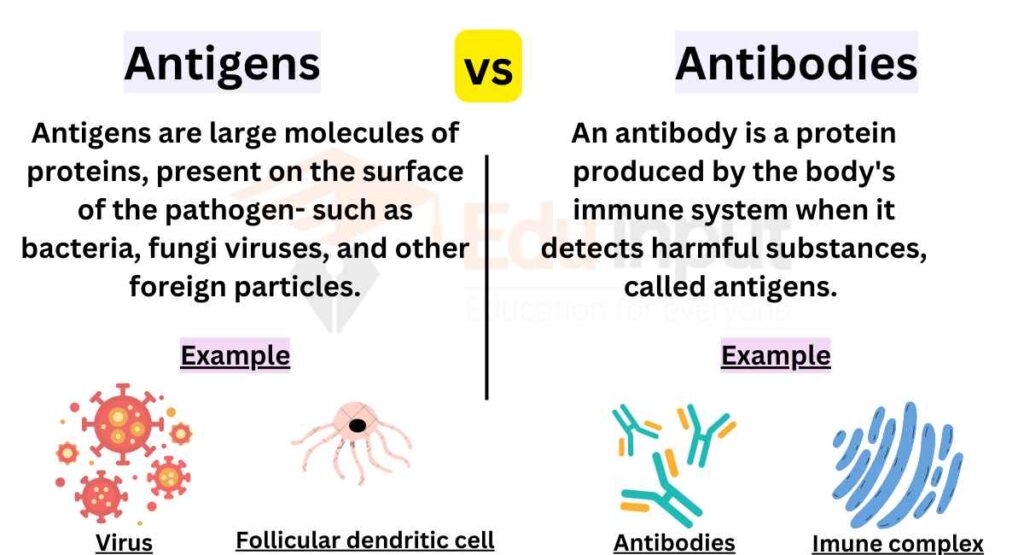
When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens . Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; The other is to elicit an immune. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces.
from eduinput.com
The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: The other is to elicit an immune.
Differences Between Antigens And Antibodies
When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. The other is to elicit an immune. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens;
From slideplayer.com
The Lymphatic System and Immunity ppt download When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. One is to bind specifically to their target. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From humanbio.org
9a4 Antibody Mediated HumanBio When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. The other is to elicit an immune. This binding can inhibit pathogen. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From step1.medbullets.com
Antibodies Immunology Medbullets Step 1 When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.wise-geek.com
What is Molecular Immunology? (with pictures) When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. The other is to elicit. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.shalom-education.com
Monoclonal Antibodies GCSE Biology Revision When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. The antibody recognizes a unique. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From teachmephysiology.com
Antigen Processing and Presentation TeachMePhysiology When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. The other is to elicit an immune. The. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From fineartamerica.com
Antibodies And Antigens, Illustration Photograph by Gwen Shockey When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. This binding can inhibit pathogen. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.science-sparks.com
Natural and Artificial Immunity Immunology for Kids When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.cancer.gov
Monoclonal Antibodies NCI When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab). When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.linstitute.net
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记2.5.8 Antibodies翰林国际教育 When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.elevise.co.uk
B3 E) Fighting Diseases The Immune System AQA Combined Science When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. The other is to elicit an immune. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key.. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.drugtargetreview.com
Antibody effector functions are key to combatting COVID19, finds study When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From philschatz.com
Overview of Specific Adaptive Immunity · Microbiology When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; The other is to elicit an immune. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags);. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From uberstrainer.com
What’s the Difference Between Antigens and Antibodies? When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens We will discuss the different ways in which antigens. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From eduinput.com
Differences Between Antigens And Antibodies When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens The other is to elicit an immune. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; The antibody. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From askanydifference.com
Antigens vs Antibodies Difference and Comparison When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; Each antibody binds to a specific antigen in a highly specific interaction analogous to a lock and key. Antibodies (abs) have two distinct functions: The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. The other is to elicit an immune. Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.amgen.com
10 Things to Know About Antibodies Amgen When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, called an antigen. Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens; Each tip of the “y” of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a lock. This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. One. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.
From www.amgen.com
10 Things to Know About Antibodies Amgen When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens This chapter describes different techniques that profit the specificity of the interaction between antibodies (ab) to a. One is to bind specifically to their target antigens (ags); Opsonization starts with antibodies (immunoglobulins or ig) attaching to specific antigens on pathogen surfaces. This binding can inhibit pathogen infectivity by blocking key extracellular sites, such as. We will discuss the different ways. When Antibodies Attach To Specific Antigens.